Several types of fungus on human feet are called mycoses. When the skin is affected, the disease refers to the group of dermatomycosis (epidermophytosis, trichophytosis), since the dermis is translated from the Greek as skin. If the nail is affected, the disease is defined as onychomycosis.

Causes of the disease
Foot fungus is a common disease that occurs throughout the world. More common in cities than in rural areas. The risk group for foot fungus includes athletes, shower workers, and hot shop workers. Children have thinner skin that is not protected from external factors, so they are also susceptible to fungal infections. Another reason is increased sweating of the feet, as a result of diseases in the body or a congenital characteristic. Dermatologists believe that the risk of foot fungus increases with age. Factors that contribute to the disease:
- wearing uncomfortable synthetic leather closed shoes;
- warm environment with high humidity, typical when wearing shoes;
- violation of blood supply to the extremities;
- frequent visits to crowded places;
- a weak or poorly functioning immune system;
- wearing strangers shoes.
Rapid infection
Dermatomycosis of the feet is easily transmitted in public places from a sick person to a healthy person. Infection occurs through contact surfaces: floors, household items, personal hygiene items, someone else's shoes. The fungus is transmitted by direct contact, it multiplies very quickly, which is why it is so easy for them to become infected. The situations of fungal transmission in hairdressing salons through tools during a pedicure, as well as towels, are not excluded. The disease affects the skin of the feet. It is especially common in men, as they spend most of their time in closed shoes. Frequent visits to gyms, bathrooms, military service, where you don't always have to wear your own shoe size; all this creates favorable conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic bacteria. An unventilated area of the room is beneficial for the reproduction of disease-causing fungi. The spread of pathogenic flora is very fast. The place where the fungus predominates is the toes and the interdigital spaces. Saunas and baths are characterized by high humidity and high temperatures, which is ideal for the development of pathogenic microflora.
Fungal infection can be direct and indirect. Directly, you can become infected through direct contact with a sick person. Indirect contamination involves the use of objects that have been used by a sick person.
Manifestations of mycosis
The first symptom of the disease is the appearance of scales on the skin in the area of the feet. Through these elements, infection occurs. Increased sweating is a favorable factor for the reproduction of microbes, since the altered composition of sweat becomes a nutrient for the growth of pathogenic flora.
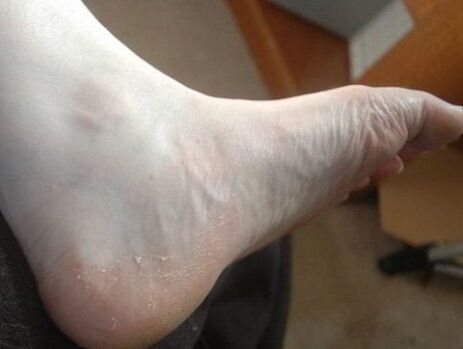
Dirt and thread debris from socks also collects between the toes. When a fungal infection is added to the listed factors, redness occurs there. The affected area begins to itch unbearably, causing discomfort to the person. The skin begins to peel off, causing painful cracks to appear. When walking, there are unpleasant painful sensations due to the presence of wounds on the skin of the foot. The skin begins to thicken and the infection can spread to the nails. If left untreated, the fungal infection spreads and affects the nails, destroying them. The nail plate first changes its color to a white tint. Later, it can come off. Gaps form between the nail plate and the nail bed. With a fungus on the feet, an unpleasant smell appears. In winter, when wearing closed shoes, the leg is not ventilated, the intensity of the foot injury increases. For the treatment of this pathology, an accurate formulation of the correct diagnosis is necessary, because there are many types of fungal pathogens.
The main types of diseases.
- The membrane type (intertriginous form) is the most common. A fungal infection is seen between the fifth and fourth toes. Gradually, the skin acquires a scaly structure with elements of cracks. Sometimes a bacterial infection attaches itself to the fungus, causing even more damage to the skin on the legs.
- Moccasin type. Manifested by pain in the foot. So the skin becomes thicker, thicker and cracks. Serious fungal lesions capture the nails, which over time can begin to crumble and detach.
- Vesicular type (dyshidrotic form). It is manifested by the appearance of blisters under the skin, filled with fluid. It often progresses along with a bacterial infection.
Types of mushrooms in the photo of the legs with names
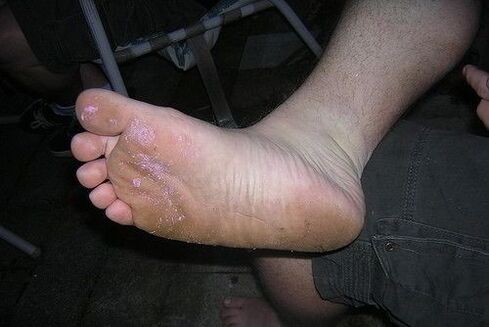
There are several types of fungi, they correspond to various diseases. There are four most common types of fungus that cause foot damage.
- Trichophyton rubrum (Trichophytonrubrum) is plagued with rubrophytosis.
- Trichophyton interdigitale (Trichophyton interdigitale) affects the skin between the toes, involving the entire foot in disease. Causes epidermophytosis disease.
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes leads to complete epidermophytosis.
- Candida albicans is a female fungus. It causes yeast infections of the feet, but this is rare.
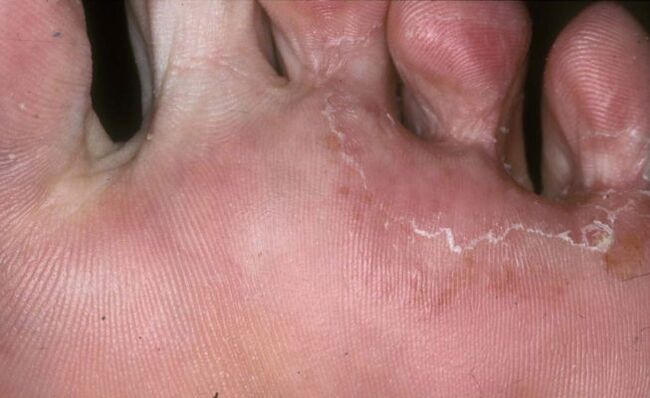
Epidermophytosis and trichophytosis (rubromycosis) are skin diseases collectively called mycoses of the feet, caused by parasitic fungi of the genus dermatophytes.
Classification
Dermatophyte fungi:
- microsporum;
- epidermophyton;
- t.
Molds that cause fungal diseases:
- hendersonula;
- altemaria;
- s.
Yeast pathogenic fungi:
- pityrosporum;
- candida;
- cryptococcus;
- malassezia;
- coccidoides;
- histoplasma;
- w.
Precautionary measures

Since fungi love a warm and humid habitat, it means that these conditions need to be violated to get rid of them. Therefore, to prevent fungus, the feet must be clean and dry. It is important to change your socks and dry your shoes on time. There are special antiperspirants for sale that will block the development of pathogenic microflora. It is better to choose leather shoes to maintain normal metabolic processes between the feet and the environment. The foot will sweat less and the conditions for the reproduction of fungi will not be created. It is advisable to wear socks at home, which you take off and wash, while microbes and dirt will accumulate on house shoes.
It is necessary to use only your own things, since you do not know the presence of someone else's diseases. Your immunity may not be able to cope with pathogens and it becomes infected. You need to air your shoes more often. When visiting public places, it is advisable to carry personal hygiene items with you. Never walk barefoot on the floor in pools and showers. Using prophylactic antifungal creams and ointments also helps. After all, swimming pools, locker rooms, saunas, and other rooms with high humidity are breeding grounds for fungi. At home, in the bathroom, it is better to refuse porous carpets.
At-risk group
There are people who are more susceptible to this disease than others. This can be due to problems in the body, such as:
- overweight;
- violation of blood circulation in the legs;
- flat feet and foot deformities;
- impaired immune system;
- people under stress;
- after antibiotic treatment.
Diagnosis of fungal disease of the feet.
The doctor conducts a detailed examination of the foot, asks complaints. Skin samples are taken from the patient to test for the presence of fungus. You get a skin fragment with a minor scratch, specially made, on the foot. For analysis, the nail is cut from the place infected with the fungus. The presence of mycosis is determined by special tests. To identify the type of fungus, it is cultivated, that is, it is cultivated. In rare cases, with an advanced stage of the disease, the patient may be prescribed a biopsy. In this case, the prepared material is examined under a microscope.
Treatment methods
To obtain results from the treatment, it is necessary to clarify the type of fungus and the presence of infections, if any, have joined it. The degree of damage is also taken into account.
The basis of membrane-type treatment seems to apply antifungal drugs to the affected area. It is convenient to do it even at home. These drugs stop the growth of bacteria or slow the spread of the disease. Many of these medications are available without a prescription. The action of the substances occurs locally, at the site of application on the affected skin. It is important to monitor the dynamics of the treatment, if there is no improvement, the medicine may not be helping you.

If there is no effect of the agent used, then it is necessary to consult a dermatologist again about the appointment of another treatment. You may need to prescribe a stronger medication. In especially severe cases of the course of the disease, tablets are prescribed. Many medications have side effects, so it is necessary to monitor blood counts during pill treatment. The fungus is very difficult to cure completely, as it can reappear. Treatment should not be interrupted, otherwise the fungi may show resistance to the components of the drug that affect them. During the treatment, it is necessary to monitor the cleanliness and dryness of the foot. With a moccasin-like form of infection, onychomycosis, that is, damage to the nails, occurs very often. Due to the fact that the skin on the leg is thickened and it is more difficult for drugs to penetrate inside, this disease is more difficult to cure. In this case, standard drugs "do not work" and additional therapy is prescribed in the form of pills. Onychomycosis: damage to the toenails by a fungus of the genus dermatophytes. The disease can also be caused by yeasts and molds. There are several types of onychomycosis:
- Distal subungual. Depending on the area of the injury of the nail plate, three degrees of damage are distinguished. If the nail occurs in one section and is conditionally divided into three parts (in depth), then the lesion up to two-thirds of its volume will correspond to the first two stages of the disease. And when more than 2/3 of the nail is affected by the fungus, this is already the third degree. In this case, the root of the nail (womb) is involved in the disease process and sometimes also the skin folds on the sides of the nail, called periungual ridges;
- proximal subungual. The defeat of the back of the nail plate, where the hole is;
- surface white. This type of onychomycosis is common in the feet;
- total dystrophic. The last final stage.
In the vesicular type, the doctor may prescribe the removal of the upper part of the blisters. Then all the liquid that comes out of them is erased. This area is dried, an antifungal cream or a special compress is applied to it. If the presence of a bacterial infection is determined, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by a fever. Acute infections respond better to treatment than chronic and slow fungal processes. In severe cases, hormonal drugs are prescribed. Antifungal medications are taken until complete recovery. It happens that not all fungi die, and when the drugs are canceled, a relapse of the disease occurs.
If the patient is not treated, the disease will become chronic and a serious bacterial infection will develop. In addition to the foot, the skin on the toes may be affected by the disease.
Traditional medicine offers compresses and lotions for the treatment of nail fungus using tea tree oil, which has an anti-inflammatory effect, as well as garlic. Washing with regular detergents does not always kill pathogenic bacteria. To remove fungus from clothing, clothing should be washed in hot water or, if possible, boiled. We recommend using bleach and hot ironing.
























